Is It Hormones or Fat? Diagnosing and Treating Gynecomastia the Right Way
Understanding the Root of the Problem
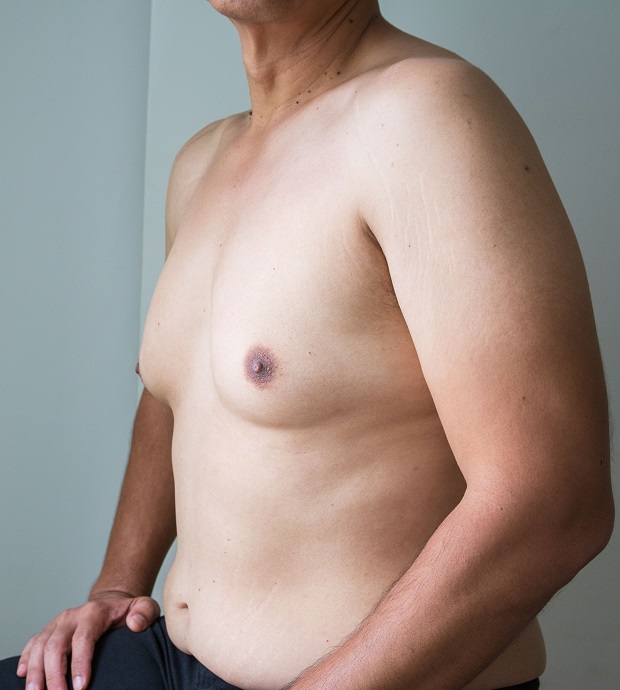
Gynecomastia is a condition many men quietly struggle with, unsure whether their chest changes stem from fat accumulation or hormonal imbalances. This uncertainty not only affects physical appearance but can also erode self-esteem and confidence. Often, men notice a puffiness or firmness in their chest area and quickly dismiss it as weight gain, not realizing that the underlying issue could be glandular. Gynaecomastia treatment depends largely on an accurate diagnosis, which makes understanding the difference between fat and true glandular tissue crucial.
One of the key distinctions is how the tissue feels. Excess fat tends to be soft and evenly distributed, whereas gynecomastia presents as firm or rubbery tissue beneath the nipple. It might even feel slightly tender or painful to the touch. While both scenarios might coexist—especially in overweight individuals—it’s the presence of glandular tissue that defines gynecomastia. But what causes this hormonal shift? It could be natural changes during puberty, aging, or side effects of medication. Sometimes, liver or thyroid issues contribute, and in rare cases, tumors can trigger hormone imbalances. For these reasons, consulting a doctor for an evaluation is always the safest route.
Hormonal Imbalances: The Silent Culprit
Hormones, especially the balance between estrogen and testosterone, play a central role in the development of gynecomastia. Men produce both hormones, but testosterone usually dominates. When this balance tips—either due to increased estrogen levels or a drop in testosterone—breast tissue can begin to grow. This is particularly common during puberty and in older age. In teenagers, gynecomastia usually resolves on its own as hormone levels stabilize. In older men, declining testosterone and increased body fat (which converts testosterone to estrogen) can create the ideal conditions for glandular breast development.
Certain medications are known to affect hormone levels as well. Anti-androgens used for prostate issues, anabolic steroids, some antidepressants, and even heart medications can disrupt hormonal balance. Additionally, alcohol, marijuana, and certain herbal products like tea tree oil have been linked to gynecomastia through their effects on hormones. In these cases, identifying and discontinuing the trigger may resolve the issue—but this must always be done under medical supervision.
When It’s Just Fat: Pseudogynecomastia
Not all enlarged male chests are the result of hormonal imbalance. In many cases, particularly among those who are overweight or obese, what appears to be gynecomastia is actually pseudogynecomastia. This refers to excess fat deposition around the chest area without any underlying glandular growth. While it may look similar in appearance, pseudogynecomastia doesn’t involve the dense, fibrous tissue that characterizes true gynecomastia. It is a cosmetic issue rather than a hormonal one.
That said, even though it’s "just fat," it can have the same psychological impact as gynecomastia. Men may feel self-conscious, avoid certain clothing, or shy away from social activities like swimming. Weight loss and regular exercise can reduce fat in the chest area, but results may vary. Some men find that despite losing significant weight, the chest area still appears disproportionately large. In such cases, surgical options like liposuction may be considered to remove the remaining fat and restore a flatter chest profile.
Diagnosis: The First and Most Important Step
Before diving into treatment options, getting a correct diagnosis is essential. Doctors typically begin with a physical examination to feel the type of tissue present. They may ask about the onset of symptoms, lifestyle habits, medications, and any history of hormone-related conditions. Blood tests can measure hormone levels, and imaging studies like ultrasound or mammography may be used to distinguish between fat and glandular tissue or to rule out tumors.
In adolescents, watchful waiting is often advised as many cases resolve naturally within a year or two. However, if the condition persists beyond that or occurs in adulthood, further intervention may be necessary. Early detection and diagnosis not only help in addressing the issue more effectively but also rule out more serious underlying health conditions.
Treatment Options: From Conservative to Surgical
Once diagnosed, treatment depends on the cause and severity of the gynecomastia. If medication or substance use is the culprit, discontinuing it might reverse the condition. Hormone therapy, such as using anti-estrogens or testosterone replacement, is sometimes used, but its effectiveness varies. These options are usually reserved for those with clearly identified hormonal causes and under the care of an endocrinologist.
For persistent or severe cases, surgical intervention is the most definitive solution. Male breast reduction surgery involves the removal of glandular tissue, and in some cases, fat through liposuction. This outpatient procedure offers a high success rate and significantly improves the chest’s appearance. Recovery is typically quick, with most men returning to normal activity within a week or two. Results are long-lasting and can be life-changing for men who’ve struggled with the emotional burden of gynecomastia for years.
On the other hand, for pseudogynecomastia, non-surgical fat reduction techniques may be effective. These include liposuction or newer, minimally invasive options like cryolipolysis (fat freezing). However, lifestyle modification—regular cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and a healthy diet—remains the cornerstone of managing pseudogynecomastia.
Moving Forward With Confidence
Whether caused by hormones or fat, gynecomastia can significantly affect a man’s self-image and quality of life. The key to effective management lies in distinguishing between true gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia and understanding the root cause. Thankfully, modern diagnostic tools and a variety of treatment options offer real solutions.
What’s most important is not ignoring the issue or brushing it off as just a “normal part of aging” or “just fat.” Men today have access to more information and resources than ever before. Consulting a qualified healthcare provider, ideally someone with experience in male breast conditions, is the first and most empowering step toward resolution.
Taking control of your health and appearance is not about vanity—it’s about feeling comfortable in your own body. Whether the answer lies in hormone balancing, fat reduction, or surgery, there is a path forward. And with the right approach, gynecomastia doesn't have to be a lifelong burden.


Comments
Post a Comment